Surge protectors work by diverting excess voltage away from your electronics during unexpected power spikes. Here’s how they do it: 1) They use components like MOVs to absorb energy and convert it into heat. 2) GDTs divert too much voltage to the ground. 3) Thermal fuses disconnect the protector to prevent overheating. However, keep in mind that these devices need regular checks and replacements to stay effective. Stick around, and you’ll find out more about choosing the right surge protector!
Key Takeaways
- Surge protectors use components like MOVs and GDTs to absorb and divert excess voltage away from electronics.
- They activate within microseconds to respond quickly to voltage spikes and prevent damage.
- Proper grounding and placement near sensitive devices enhance their effectiveness in protecting electronics.
- Regular maintenance, including visual inspections and replacing units every 3 to 5 years, is crucial.
- Surge protectors come in various types, each designed for specific applications and voltage levels.
Understanding Power Surges

When it comes to understanding power surges, you might be surprised to learn how much of a role they play in our daily lives. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Surge Causes: These can stem from lightning strikes, heavy appliances, and even electrical grid disturbances. Imagine your fridge kicking on and suddenly, zap!
- Surge Effects: The aftermath isn’t pretty. Surges can overload circuits, frying electronics or causing gradual wear and tear. Even devices left off but plugged in aren’t safe!
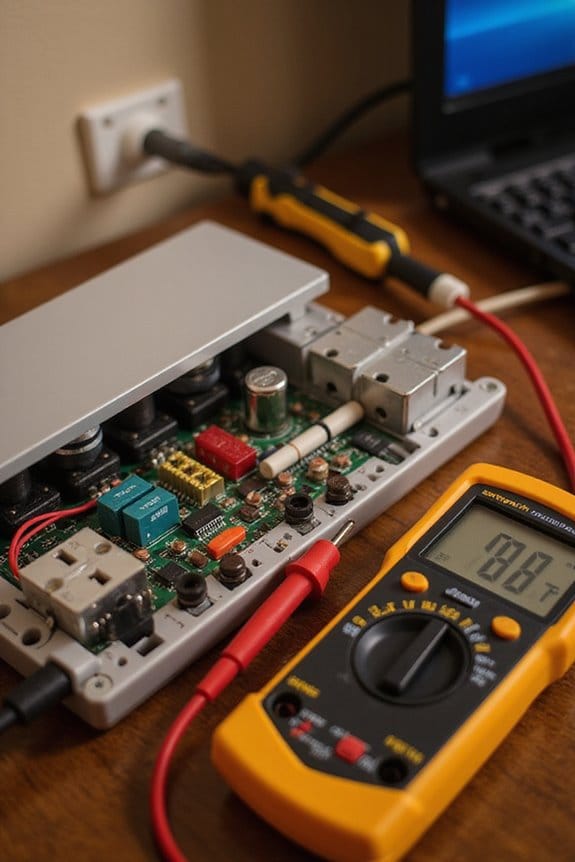
Components of Surge Protectors

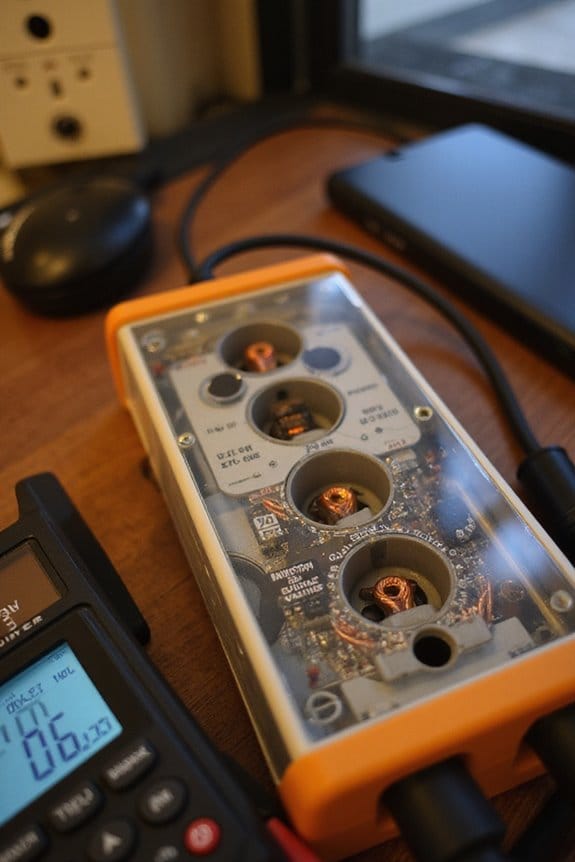
Power surges are a real headache, but luckily, surge protectors have our backs. Here are the key components that keep our devices safe:
- MOV Functionality: The Metal Oxide Varistor is like the first responder. It absorbs excess energy by allowing current to flow when voltage spikes, converting it to heat.
- GDT Activation: The Gas Discharge Tube kicks in during higher voltage surges, safely diverting excess current to the ground, providing an extra layer of protection.
- Thermal Fuse: This little hero prevents overheating by disconnecting the surge protector if temperatures get too high, reducing fire risks.
- Protective Enclosure: A sturdy outer shell shields everything inside, ensuring no moisture or dust can mess with our surge protectors. Regular checks on this enclosure can save you a lot of trouble!
Types of Surge Protection Devices

Surge protection isn’t one-size-fits-all, so let’s break down the different types of Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) available. Here’s a quick device classification:
- Type 1 SPDs: Installed on the line side of the main service entrance, these handle surges up to 1000 volts. They’re perfect for protecting against lightning strikes.
- Type 2 SPDs: Known as transient voltage surge suppressors, these go on the load side and manage surges up to 600 volts, ideal for everyday electrical switching.
- Type 3 SPDs: These plug-in devices guard specific electronics like computers. They’re your last line of defense against residual surges.
Each type serves a unique purpose, so you’ll want to choose based on your specific needs. It’s like picking the right tool for the job!
Operational Requirements for Effectiveness
To guarantee that surge protectors work effectively, it’s vital to take into account a few key operational requirements. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Surge Coordination: Make sure your surge protectors match the specific electrical system. This avoids damage and guarantees they work when needed.
- Grounding Requirements: Proper grounding is essential. Connect your surge protectors to a well-grounded outlet. This gives excess voltage a safe path to dissipate.
- Installation: Place your surge protectors close to sensitive devices. Short lead lengths mean less voltage gets through.
- Response Time: Choose protectors that activate fast—within microseconds—to keep your electronics safe.
Maintenance and Limitations of Surge Protectors

While it might be easy to forget about surge protectors once they’re plugged in, keeping an eye on their maintenance and limitations is essential for protecting your valuable electronics. Here are some tips:
- Check Indicator Lights: These lights can signal faults. If they’re off or blinking, it’s time to investigate.
- Visual Inspections: Look for any damage or discoloration. Don’t ignore these signs!
- Replacement Frequency: Aim to replace your surge protector every 3 to 5 years, or sooner after major surges.
- Avoid Overloading: Don’t daisy-chain them; it can lead to failure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Surge Protectors Be Used Outdoors?
Yes, I can confirm that surge protectors can be used outdoors, especially those with outdoor ratings. Their weather resistance guarantees they withstand harsh conditions, protecting my devices from surges caused by storms and other environmental factors.
How Do I Choose the Right Surge Protector?
When I choose a surge protector, I consider surge ratings and the outlet types I’ll be using. It’s essential to match the protector’s joule rating with my devices for best safety and performance.
Do Surge Protectors Protect Against Power Outages?
Imagine my laptop shutting down during a storm. Surge protectors don’t guard against power outage effects; their surge protection mechanisms only handle voltage spikes, leaving my devices vulnerable when the power goes out.
Are Surge Protectors Safe for All Electronics?
I’ve found that surge protectors are generally safe for most electronics, but compatibility varies. It’s crucial to choose the right surge protector types based on your devices’ needs to guarantee ideal protection and performance.
What Happens When a Surge Protector Fails?
When a surge protector fails, I notice my devices become vulnerable, as the protection limits are breached. It’s alarming to think that internal damage could lead to overheating or even potential electrical fires.





